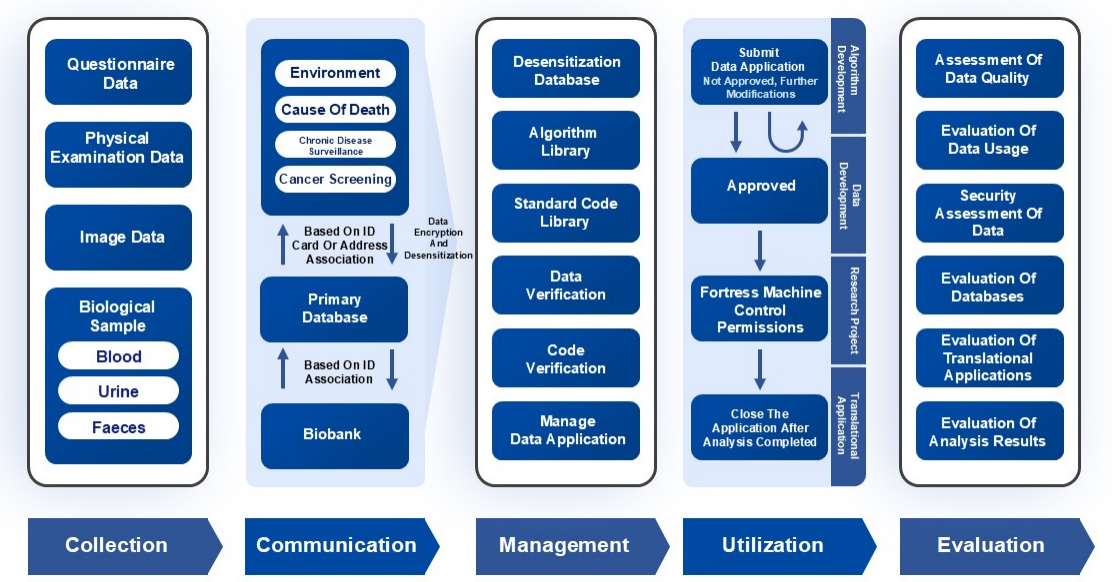
The Data Management and Analysis Platform aims to build a five-in-one standardized health big data information platform for data collection , communication, management, utilization and evaluation. This platform converges heterogeneous data from sources such as biobank, epidemiological data, genomic data, clinical data, and biomarker data. It achieves seamless data integration through unified data standards and in-depth governance, while standardizing and tagging the full range of data assets, supports various scientific research projects, including data development and algorithm development, through intelligent data application services. By implementing hierarchical data access permissions, it serves different user categories such as logistics, operation and maintenance, data administration, and research teams, exploring and promoting the construction of a shared platform. Furthermore, it enhances the quality of the big data information platform through data aggregation assessment, assessment of data quality, and evaluation of data usage.
Currently, we have built three groups of dedicated high-performance server clusters for data analysis and computing, with a total of 7PB storage space capacity, and can be further expanded and upgraded according to future usage demands. These clusters are equipped with dual-redundant control systems, firewalls, data backup systems, and UPS uninterruptible power supplies, providing domestically leading supercomputing capabilities and disaster recovery performance. Up to 500 terabytes of genome-wide data have been stored. At the same time, it provides support for the health examination big data platform that encompasses more than 2.1 million physical examinations for a total population exceeding one million. It enables synchronous transmission and off-site backup of data between the Zijingang campus data center of Zhejiang University and medical institutions nationwide. With the support of supercomputer computing power, this platform utilizes advanced bioinformatics and biostatistical methods to help establish individualized risk prediction models that cover the whole chain of tumors, and convert them into a series of artificial intelligence tools for predicting personal disease risks. It provides powerful technical support for establishing of early identification methods for high-risk population.